What is distortion? What's wide dynamic technology?
What is distortion?
distortion
——————— Camera terminology
Lens distortion is a kind of difference. The diameter of the object becomes a curved phenomenon after passing through the lens. Distortion is caused by the magnification of the lens as a function of the angle between the beam and the major axis. The farther the light is from the spindle, the greater the distortion, but if it is orthogonal to the spindle and passes through the spindle, no distortion occurs. When the magnification increases as the incident angle increases, it is called orthodontic. The magnification is called negative distortion when the angle of incidence decreases as the angle of incidence increases. In other words, if the object point is farther from the optical axis, the greater the magnification, the more orthodontic. If the object point is farther away from the optical axis, the smaller the magnification, the negative distortion occurs. Especially when the lens has a large diopter, the distortion of the image becomes severe. Because of the distortion, looking at the object, like losing the original correct shape. The method of reducing the distortion is to change the shape of the lens for a single lens, and to minimize the distortion by using the optimum shape.
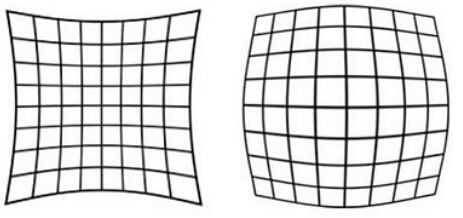
Orthodontic (pillow) negative distortion (barrel)
What is wide dynamic technology?
Wide dynamic technology
——————— Camera terminology
Wide dynamic technology is a technique that allows the camera to see the characteristics of the image in very strong contrast. When a high-luminance area illuminated by a strong light source (daylight, luminaire, or reflective) and a relatively low-intensity area such as a shadow or a backlight are simultaneously present in the image, the image outputted by the camera may appear bright, and the white area becomes white due to overexposure. The dark area becomes black due to insufficient exposure, which seriously affects the image quality. The camera's performance in the brightest and darker regions in the same scene is limited. This limitation is commonly referred to as the "dynamic range."
The "dynamic range" in a broad sense refers to the span of a changed thing that may change, that is, the area between the lowest pole and the highest pole of the change value. The description of this area is generally between the highest point and the lowest point. Difference. This is a very widely used concept. When talking about the image indicators of a camera product, the general "dynamic range" refers to the ability of the camera to adapt to the illumination of the scene in the scene, specifically the brightness (contrast) and color temperature (contrast). The scope of the change.
Wide dynamic cameras are dozens of times larger than traditional cameras with only a 3:1 dynamic range. Natural light is arranged from 120,000 Lux to 0.00035 Lux at Starlight Night. When the camera looks out of the window from the inside, the indoor illumination is 100 Lux, and the illumination of the outside scenery may be 10,000 Lux, compared to 10,000/100 = 100:1. This contrast makes it easy for the human eye to see because the human eye can handle a contrast ratio of 1000:1. However, it is a big problem to deal with it with a traditional closed-circuit surveillance camera. The traditional camera has only 3:1 contrast performance. It can only choose to use the 1/60 second electronic shutter to get the correct exposure of the indoor target, but the outdoor image. It will be cleared (all white); or alternatively, the camera will select 1/6000 seconds to get the perfect exposure for the outdoor image, but the indoor image will be cleared (all black). This is a long-standing flaw since the camera was invented.
Dynamic Range: The Dynamic Range is simply a detailed representation of the highlights and shadows of a digital camera, that is, extreme black and white performance. Everyone may encounter such a situation in the shooting. The contrast between light and dark is too strong. Especially in the case of backlighting portraits, the richer the level of representation, the wider the color space involved. The greater the dynamic range of a digital camera, the more detail it can record at the same time in dark detail and highlight detail.

